Pages
▼
Saturday, June 30, 2012
How to disable lock screen in Linux Mint 13 Cinnamon
In Linux Mint Cinnamon, if you are idle for a while, you computer screen will blank out and the lock screen feature will be activated and you will have to enter your password to re-access your computer. If you dont want to enter the password all the time, you can disable the lock screen feature easily.
To do so in Cinnamon, you can use the familiar tool gconf-editor, but you will have to install it first. Just open the terminal and run the following command to install gconf-editor:
sudo apt-get install gconf-editor
Next, hit Alt + F2 and type "gconf-editor":
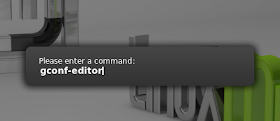
The configuration window will appear, on which you go to desktop > gnome > lockdown and check the option "disable-lock-screen":
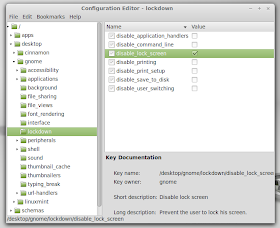
And from now, the computer screen will only blank out when idle without the lock screen. To re-access the computer, all you need to do then is to press a key or move the mouse.
Calibre 0.8.58 Has Better Generated Covers
Version 0.8.58 of the e-book reader and management software Calibre was announced on June 29th, with some important new features and fixes.
Calibre 0.8.58 brings some improvements for generated covers and introduces quite a few new drivers for various devices.
Highlights of Calibre 0.8.58:
• Texture for calibre generated covers has been added;
• Drivers for Sogo SS-4370, HTC G2 and Lenovo ThinkPad Tablet have been added;
• Search to the Manage tags/series/etc. dialogs has been added;
• Support for images embedded in the HTML has been added;
• A more robust handling of EINTR during IPC has been implemented;
• A bug that could cause corrupted output when doing an EPUB/OEB to EPUB conversion has been fixed.
• News sources have been improved.
A complete changelog can be found in the official announcement.
Download Calibre 0.8.58
Phoronix Test Suite 4.0 Milestone 4 Available for Download
The third milestone release of the Phoronix Test Suite 4.0 (Suldal) has been announced today by Michael Larabel.
Phoronix Test Suite is the most comprehensive benchmarking and testing platform available for Linux, and designed to carry out qualitative and quantitative benchmarks in a clean, reproducible, and easy-to-use manner.
Highlights of Phoronix Test Suite 4.0 Milestone 4:
• Support download caches at /run/media/*/*/download-cache/ has been added;
• Set SKIP_TEST_SUPPORT_CHECKS=1 environment variable for debugging purposes to run tests on unsupported platforms;
• The software only renders as much room for pts_OverViewGraph as there are for what will be rendered (bar graph values);
• DVD drives don't get reported on BSD operating systems when requesting disk drives;
• Various alterations have been implemented;
• Graphics processor detection on Solaris 11 11/11 for non-NVIDIA GPUs has been improved;
• Support for handling i915_energy monitor reading in microJoules for each test run has been added;
• A timer support for individual test runs within the module has been implemented.
Download Phoronix Test Suite 4.0 Milestone 4
Install Original Linux Mint 13 Maya Theme & Icons On Ubuntu 12.04 Precise Pangolin
In this tutorial, we will help you install the original Linux Mint 13 Maya theme and icons on Ubuntu 12.04 (Precise Pangolin). The credit for this theme goes here. To make the installation easier of this theme pack, we have added it to our custom PPA. Here is a screenshot of this theme under Ubuntu:
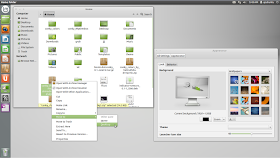
To install Mint Maya theme and icons, open the terminal and run these commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:upubuntu-com/themes
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install mint-maya-pack
Let's now enable it with these commands (Ubuntu logo in the Unity launcher will also be changed):
sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/inst-mint.sh
sh /usr/bin/inst-mint.sh
sudo cp -a /usr/share/icons/launcher_bfb.png /usr/share/unity/5/launcher_bfb.png
Log out and log back in to finsih the installation.
To restore default Ubuntu theme and logo as well as uninstalling the Mint theme and icons, run the following commands:
sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/rem-mint.sh
sh /usr/bin/rem-mint.sh
sudo cp -a /usr/share/icons/def-ubuntu/launcher_bfb.png /usr/share/unity/5/launcher_bfb.png
sudo apt-get install ppa-purge
sudo ppa-purge ppa:upubuntu-com/themes
sudo apt-get remove mint-maya-pack
Enjoy!
Mandriva Foundation Structure Illustrated, OpenMDV Intro'd
Mandriva Open Source Relations Manager, Charles Schulz, today tried to clarify the foundation's vision of structure of community interaction and resulting products. Instead of explaining, he posted a flow-chart to illustrate the relationships between downstream and upstream projects, contributors, and the Mandriva distribution.
Schulz describes the diagram as "an attempt at describing how the project will work and what it will aim at. It displays the general logic of contributions, by and for the community but also integrates what will be external products meant to be sold by companies that are based on the software development and packaging done inside the foundation."
As you can see the still-forming Mandriva community is broken down into three main contribution sources: Rosa, Mandriva community, and Mandriva SA employees. All these will contribute to the "Share Cooker" repository. Several projects are shown pulling code out of the shared Cooker repo. MIB and Unity base their projects' on Mandriva code and are shown as pulling from Cooker, but not contributing back.
The most interesting section is the resulting products. OpenMDV, which one assumes is going to be the new name for the Open Source community release, seems to be the main focus. Rosa Linux, who offers a customized version of Mandriva, will naturally continue to pull from Cooker. And finally there's a box to symbolize a range of whatever Mandriva commercial products they may want to base on Cooker.
Schulz hopes this helps folks makes sense of the Mandriva Linux Foundation, but there still seems to be some persistent talk of Mandriva SA using Mageia code for their commercial products.
Linux Mint 13 RC Xfce Edition Has Been Released
Clement Lefebvre, father of the Linux Mint project, announced a few minutes ago, June 29th, that the Release Candidate of the upcoming Linux Mint 13 Xfce Edition operating system is available for download and testing.
Being based on Ubuntu 12.04 LTS (Precise Pangolin), Linux Mint 13 RC Xfce is built on top of the Xfce 4.10 desktop environment, it is powered by Linux kernel 3.2, and distributed as a DVD ISO image for both 32-bit and 64-bit architectures.
Highlights of Linux Mint 13 RC Xfce:
· Based on Ubuntu 12.04 LTS;
· Linux kernel 3.2;
· Xfce 4.10;
· MATE and mintMenu applets;
· Mint Display Manager;
· Artwork improvements;
· Search engines.
The following system requirements are recommended by the developers for Linux Mint 13 Xfce installations:
· An x86 processor (32-bit or 64-bit);
· Minimum 256 MB RAM;
· 5 GB of free hard disk space;
· Video card capable of 800x600 resolution;
· A DVD-ROM drive or USB port.
About Linux Mint
Linux Mint is and will always be an elegant, easy-to-use, up-to-date, 100% free and comfortable Linux operating system based on the very popular Ubuntu OS.
It offers paid commercial support to companies and individuals. Also, free community support is available from the forums and the IRC channel.
Download Linux Mint 13 RC Xfce
New Kernel Update Available for All Ubuntu OSes
Canonical announced earlier today, June 29th, in a security notice, that new Linux kernel updates for its Ubuntu 12.04 LTS (Precise Pangolin), Ubuntu 11.10 (Oneiric Ocelot), Ubuntu 11.04 (Natty Narwhal), Ubuntu 10.04 LTS (Lucid Lynx) and Ubuntu 8.04 LTS (Hardy Heron) operating systems is now available, fixing three important security vulnerabilities discovered in the Linux kernel packages by various developers.
The following vulnerability affects the Ubuntu 12.04 LTS and Ubuntu 11.10 kernels: CVE-2012-2375.
The following three vulnerabilities affect the Ubuntu 11.04 kernel: CVE-2012-2313, CVE-2012-2319 and CVE-2012-2375.
The following two vulnerabilities affect the Ubuntu 10.04 LTS and 8.04 LTS kernels: CVE-2012-2313 and CVE-2012-2319.
For details about the vulnerabilities found in the Linux kernel packages you can click on each one, as it affects other Linux operating systems as well.
The security flaws can be fixed if you upgrade your system(s) now. To apply the update, run the Update Manager application or follow these instructions: https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Security/Upgrades.
Don't forget to reboot your computer after the upgrade!


























